When your storage is running low, Windows 10’s Storage Sense function will automatically free up space. The feature purges unnecessary system files, files that have been in the Downloads or recycle bin for more than a month, and restricts access to OneDrive material to files you have used recently.
This tool is limited and does not provide the ability to manually add different places to monitor and remove files that haven’t changed in the last month, despite the fact that it can be useful for controlling storage space. You can use PowerShell and Task Scheduler to monitor and clean up files from any folder older than a certain number of days if you put non-important files somewhere else.
This post will show you how to set Windows 10 to automatically remove files that haven’t been edited in the past month or any number of days you choose. (These procedures ought to function on Windows 11 as well.)
-
Delete files older than X days on Windows 10 from PowerShell
-
Delete files older than X days automatically on Windows 10 using Task Scheduler
-
Delete files older than X days automatically from Command Prompt
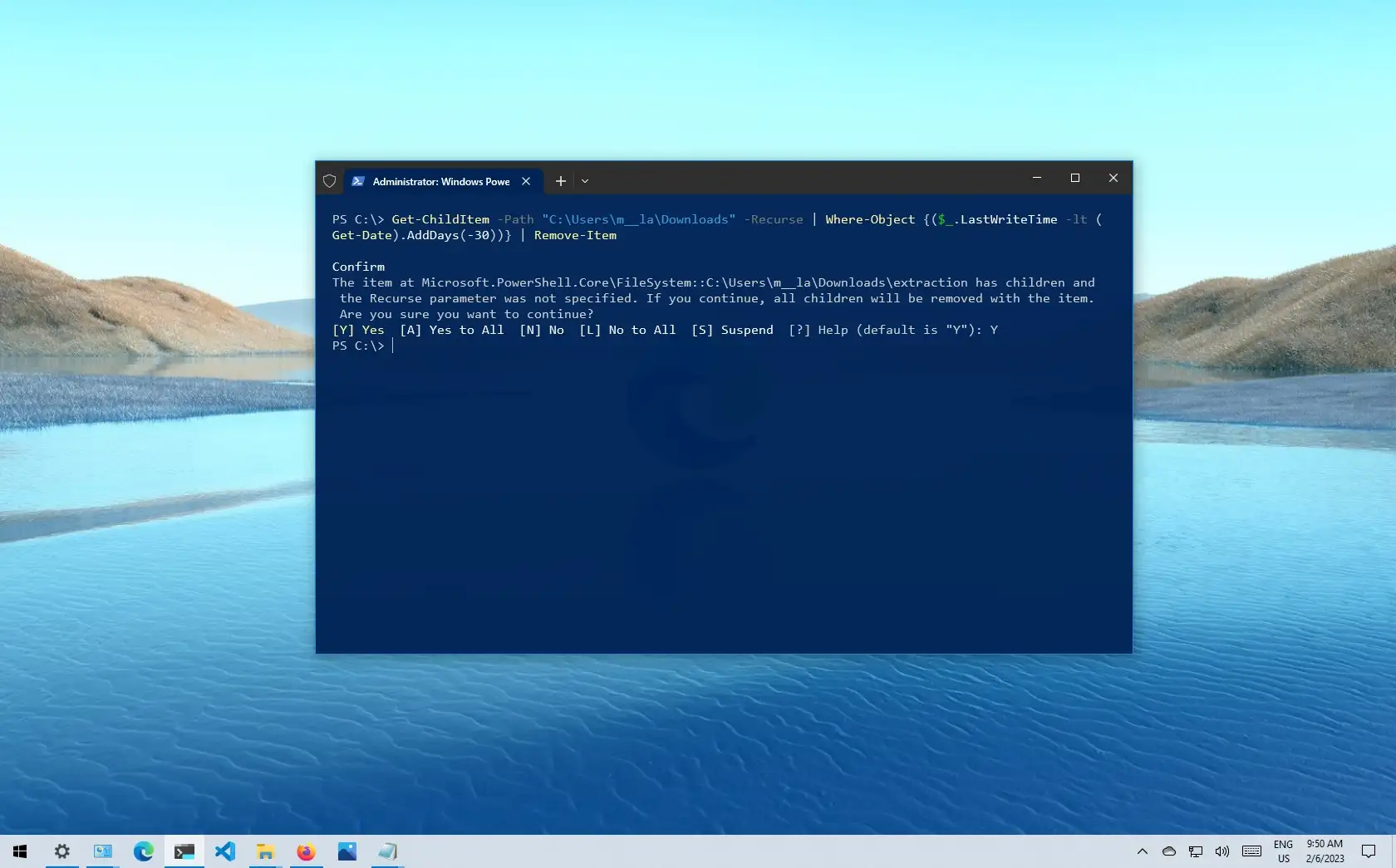
Delete files older than X days on Windows 10 from PowerShell
Use these methods to remove outdated files from a specified location in Windows 10:
Launch Windows 10.
Right-click the result of your search for “Windows PowerShell” and choose “Run as administrator.”
To remove files that haven’t been altered in the previous 30 days, type the following command and hit Enter:
Replace the folder location with “C:\path\to\folder”path in the command, and enter -30 for the file’s age since the last change.

Delete files older than X days automatically on Windows 10 from Task Scheduler
The aforementioned command lets you remove files from a folder that is more than 30 days old, but each time you wish to make room, you have to launch PowerShell and manually run the command. The process may always be automated by writing a script and using the Task Scheduler to run it on a predetermined timetable.
Create PowerShell script using Notepad
Use these instructions to write a PowerShell script that will remove Windows 10 files older than X days:
LaunchStart.
To access the experience, search for Notepad and pick the top result.
The command below should be copied and pasted into a Notepad text document:
Change thisC:\path\to\folderpath in the command by entering the folder location and -30 for the file’s age since the last change.
Select the Filemenu.
Select the “Save” option.
Use the cleanup.ps1name and extension to save the file.
Create task using Task Scheduler
Use these methods to have the PowerShell script run automatically to remove outdated files using Task Scheduler:
LaunchStart.
Click the result of your search for Task Scheduler.
(Optional) Choose the New Folder option when you right-click the Task Scheduler Library folder.
Click the OK button after confirming the folder’s name.
Choose the “Create Task” option when you right-click on the folder.
Verify the task’s name in the Name field.
Choose the “Run whether user is logged on or not” option from the Security options section of the General tab. (With this setting, the command window won’t show up when the task executes automatically.)

Turn off the “Don’t store password” setting.
Select the tab for Triggers.
Press the “New” button.
In the “Start the task” setting, choose the “On a schedule” option.
Set the task’s execution time under Settings (e.g., On time, Daily, Weekly, Monthly). The Startsettings on the right side should be specified, regardless of the choice you choose.
Press the “OK” button.

Press the Actionstab button.
Press the “New” button.
In the Actions setting, choose the Start a program option.
In the Program/script setting, type the following command:
Click the OK button after entering the following command in the Add arguments setting:
To delete files in the command, replace C:\path\to\cleanup.ps1path with the location of the PowerShell script you previously created.

To change the settings, click the Settingsstab.
Examine the choices listed below:
- Allow task to be run on demand.
- Run task as soon as possible after a scheduled start is missed.
- If the task fails, restart everything.
Press the “OK” button.
Verify your password and administrative username, if any.
Press the “OK” button.
After you finish the steps, the PowerShell script will delete the files that are older than the number of days you set when it runs on the schedule. Do not transfer the folder to an other location or change its name. If not, the task will be unsuccessful.